This website is dedicated to showcasing scientific and technological advances in complex systems modeling and instrumentation methods enabled under the rubric of the Dynamic Data-Driven Applications System paradigm. The website is a scientific community forum with hyperlinks to DDDAS research projects, virtual proceedings, related software, announcements and other news.
DDDAS Advantages From High-Dimensional Simulation
Collaboration Opportunities
- SFFP – https://afsffp.sysplus.com/
- FrontDoor – https://airforcetechconnect.org
- AFWERX – https://www.afwerx.af.mil/afventures.html
DDDAS Challenges and Processes
The key developments of the integration of the instrumentation, models, and software to enable the development of DDDAS include theory, algorithms, and computation. The theory includes mathematical advances (retrospective cost modeling – check); while the algorithms support new paradigms (e.g., ensemble Kalman filter, Particle filter, optimization techniques). The computation methods align with the developments in the continuing networked society such as non-convex optimization and data flow architectures.
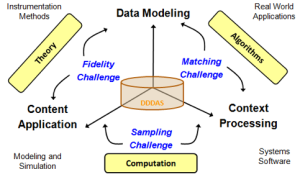
The challenges DDDAS seeks to advance include data modeling, context processing, and content application. To bring together data, context and content requires addressing issues in model fidelity such as how many parameters are needed for system control. When data is collected, it needs to be preprocessed to determine whether its inherent information matches the context. One example includes clutter reduction, sensor registration, and confuser analysis in vehicle tracking. Finally, another key challenge is that of sampling. Sampling is the multiresolution needed to monitor the situation, environment and network context to explain the content desired.
Dr. Frederica Darema, Spring Review 2014 discussing DDDAS. [video]
DDDAS Book I

Handbook of Dynamic Data Driven Applications Systems
The Handbook of Dynamic Data Driven Applications Systems establishes an authoritative reference of DDDAS, pioneered by Dr. Darema and the co-authors for researchers and practitioners developing DDDAS technologies.
 Dynamic Data Driven Applications Systems: Third International Conference, DDDAS 2020, Boston, MA, USA, October 2-4, 2020, Proceedings
Dynamic Data Driven Applications Systems: Third International Conference, DDDAS 2020, Boston, MA, USA, October 2-4, 2020, Proceedings
DDDAS-Book-I – 2nd edition — Handbook on Dynamic Data Drive Application Systems (DDDAS) (Vol. I 2ND EDITION)
The Handbook of Dynamic Data Driven Applications Systems establishes an authoritative reference of DDDAS, pioneered by Dr. Darema and the co-authors for researchers and practitioners developing DDDAS technologies. [Link]
Handbook of Dynamic Data Driven Applications Systems Volume 2
-
 Expands the scope of the methods and the application areas presented in the first volume
Expands the scope of the methods and the application areas presented in the first volume -
In-depth discussions reflecting the adoption of DDDAS paradigm from leading experts in various domain
-
Includes examples for new and advanced methods in command and control, swarm analysis, and structural health monitoring
DDDAS In The News
- Digital twins: A personalized future of computing for complex systems | Karen Willcox | TEDxUTAustin
- MIT Climate Grand Challenges
- AFOSR DDIP PI meeting for 2022 will be held at the Innovare Advancement Center on September 7-8, 2022.
- SmartGridComm (best paper award)
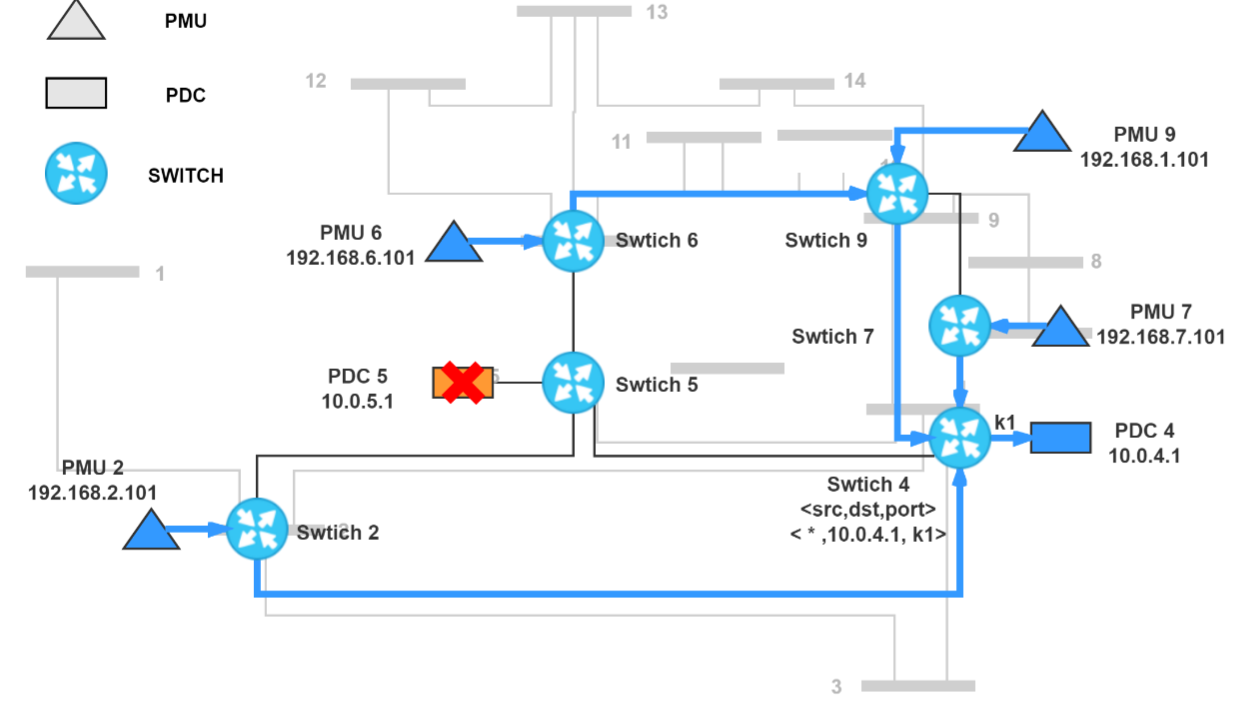 Y. Qu, G. Chen, X. Liu, J. Yan, B. Chen and D. Jin, “Cyber-Resilience Enhancement of PMU Networks Using Software-Defined Networking,” 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Tempe, AZ, USA, 2020, pp. 1-7, doi: 10.1109/SmartGridComm47815.2020.9303004.
Y. Qu, G. Chen, X. Liu, J. Yan, B. Chen and D. Jin, “Cyber-Resilience Enhancement of PMU Networks Using Software-Defined Networking,” 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Tempe, AZ, USA, 2020, pp. 1-7, doi: 10.1109/SmartGridComm47815.2020.9303004.
-
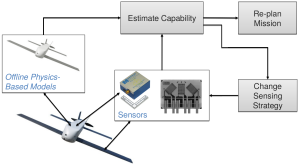
Dynamic Data-Driven Decisions: Application to a Self-Aware UAV. We are developing the methods and algorithms that enable (1) on-board dynamic decision-making for an autonomous aerial vehicle, (2) creation of a vehicle Predictive Digital Twin, and (3) illustration of the benefits of Digital Thread. The distinguishing aspect of our approach is that it is both data-driven and physics-based. Our hypothesis is that by leveraging both physics-based knowledge (through physics-based simulation data and physics-based reduced models) and dynamic data (through on-board sensors) we can issue better decisions than if we were to use data alone.
- Developing a digital twin [ details ]
- The PILOTS Programming Language: PILOTS is a Programming Language for spatiO-Temporal data Streaming applications, especially designed to be used for building applications that run on moving objects such as airplanes, cars, and so on. With very high-level specifications, users can easily build applications that take spatio-temporal data streams as an input and produce streams as outputs for use by other applications such as actuator controls, data mining/analyses/visualization, and error correction codes. These applications can be treated as components of a larger stream processing system.
-
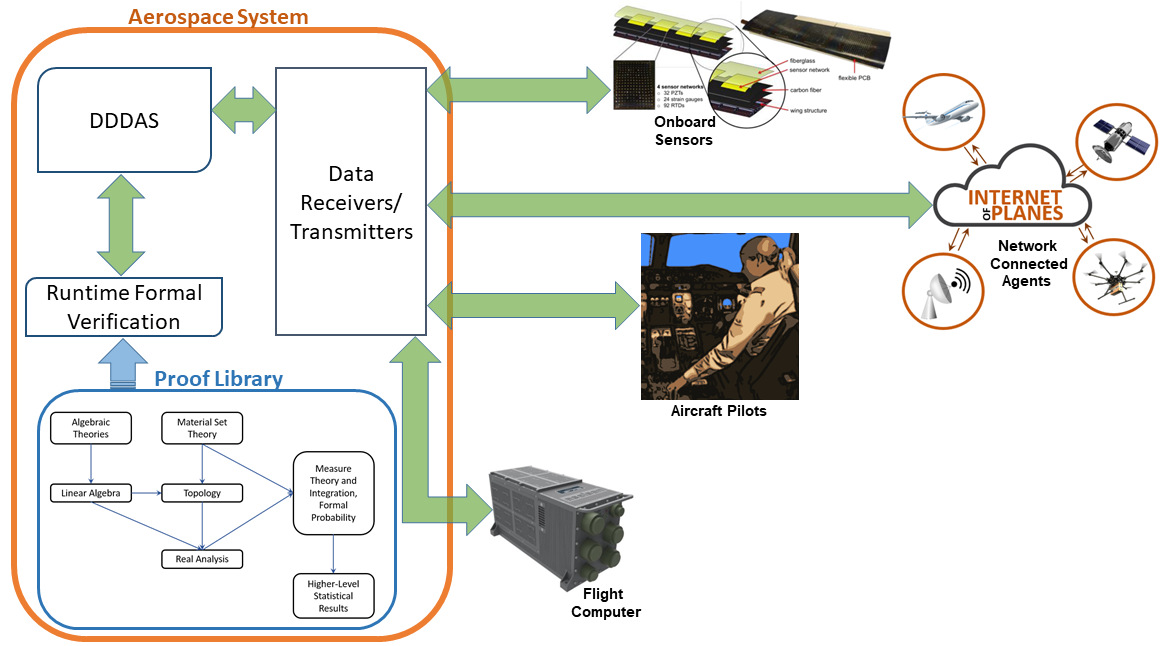
Grant Awarded to Increase Intelligence in Aerospace Systems: “We believe the next generation of aerospace systems will be able to feel, think, and react in a way that is similar to how biological systems behave.”
-
RIT researchers developing ways to use hyperspectral data for vehicle and pedestrian tracking. A classic scenario plays out in action films ranging from Baby Driver to The Italian Job: criminals evade aerial pursuit from the authorities by seamlessly blending in with other vehicles and their surroundings. The Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) has Rochester Institute of Technology researchers utilizing hyperspectral video imaging systems that make sure it does not happen in real life.
-
At SC19: Developing a Digital Twin: In the not too distant future, we can expect to see our skies filled with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) delivering packages, maybe even people, from location to location.
- Workshop report on Dynamic Data Systems (August 6-7, 2018).
Future complex systems (systems-of-systems) supporting dynamic Air Force mission needs, require adaptive data utilization, relevant resource exploitation and management, to redirect and amass the right resources, and make effective decisions at any given time with decision speed. New Science and Technology (S&T) directions provide innovation through basic research and development (R&D)to applied R&D technology transitions and demonstrate that they can create new capabilities, towards such Air Force mission critical needs. To assess the impact of such new S&T directions, the AF Chief Data Office (SAF/CO) sponsored a workshop that brought-together relevant advanced research and technology development communities to inform on S&T directions and data environments, to support the emerging Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) and Multi-Domain-Command & Control (MDC2) capability needs of the AF, and more broadly of the DoD.